Unveiling the Deceptive Tactics of the BIFROSE Linux Malware Variant
As a tech enthusiast and cybersecurity aficionado, I am always on the lookout for the latest developments in the digital landscape. Recently, a new variant of the notorious BIFROSE Linux malware has surfaced, utilizing a cunning strategy to evade detection by masquerading as a VMware domain. This discovery sheds light on the evolving tactics employed by cybercriminals to infiltrate systems and compromise sensitive information.
Delving into the Intricacies of BIFROSE
The BIFROSE malware, also known as Bifrost, has been a persistent threat since its emergence in 2004. Initially available for purchase in underground forums for exorbitant sums, this remote access trojan has been linked to the activities of the BlackTech hacking group from China. With a history of targeting organizations in Japan, Taiwan, and the U.S., BlackTech has repurposed BIFROSE for its malicious campaigns, leveraging custom backdoors like KIVARS and XBOW.
In its Linux iterations, BIFROSE, identified as ELF_BIFROSE, has exhibited a range of capabilities, including the execution of remote commands, file transfers, and manipulation.
Unveiling the Deceptive Domain Strategy
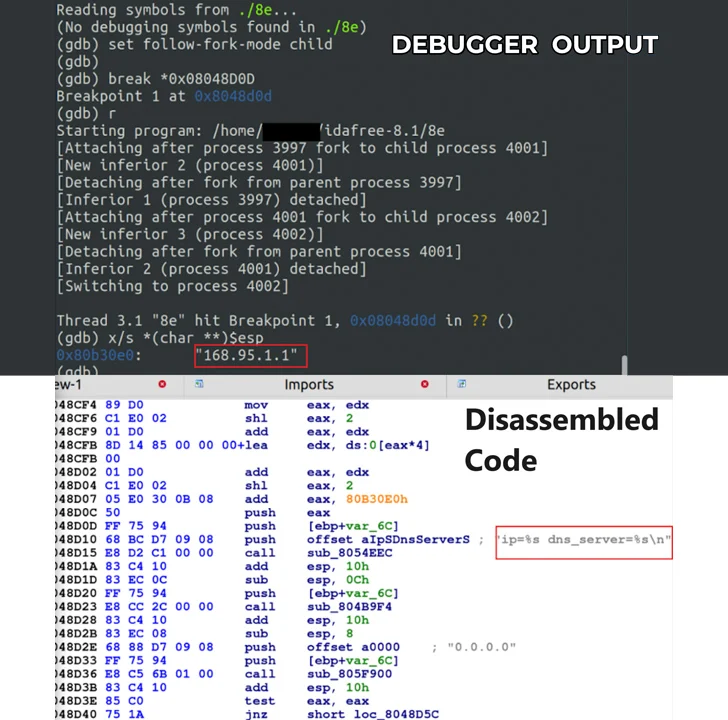
One of the standout features of the latest BIFROSE variant is its use of a deceptive domain to establish communication with a command-and-control server. By posing as download.vmfare[.]com, the malware attempts to deceive security measures by mimicking the legitimate VMware domain. This ruse is further reinforced by routing requests through a Taiwan-based public DNS resolver, underscoring the sophistication of the attackers’ evasion techniques.
Heightened Activity and Emerging Threats
Recent telemetry data from Unit 42 has revealed a surge in BIFROSE-related artifacts, signaling an escalation in cyber threats leveraging this malware. Notably, the discovery of an Arm version of the malware hints at the threat actors’ efforts to diversify their targets and broaden their attack surface.
The Implications of Deceptive Domain Strategies
The proliferation of malware variants employing deceptive domain strategies like typosquatting underscores the need for enhanced vigilance and proactive cybersecurity measures. As threat actors continue to refine their tactics and evade detection, organizations and individuals must remain vigilant and adopt robust security protocols to safeguard their digital assets.
Embracing Vigilance in the Face of Evolving Threats
In conclusion, the emergence of the new BIFROSE Linux malware variant underscores the ever-evolving nature of cybersecurity threats. By staying informed, adopting best practices, and remaining vigilant against deceptive tactics, we can fortify our defenses and mitigate the risks posed by sophisticated malware campaigns.